In November, EMC released RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines 4.2 (RP4VM) which allows replicating virtual machines with virtual machine level granularity. Recover Point for virtual machines is a new competitor of VMware Site Recovery Manager and Zerto Virtual Replication.
Some main features:
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO) - zero or seconds. (Sync or async replication available)
- RecoverPoint for VMs is storage-agnostic. Any storage supported by VMware (including FC, FCoE, iSCSI, NAS, and DAS) is supported by RecoverPoint for VMs.
- Enable automated discovery, provisioning and orchestration of DR workflows, including test, failover and failback of a single VM or VMs group
- RP4VM can replicate source RDMs (Raw Device Mappings) to target VMDKs and source
VMDKs to target RDMs. - WAN compression and de-duplication = bandwidth consumption optimization
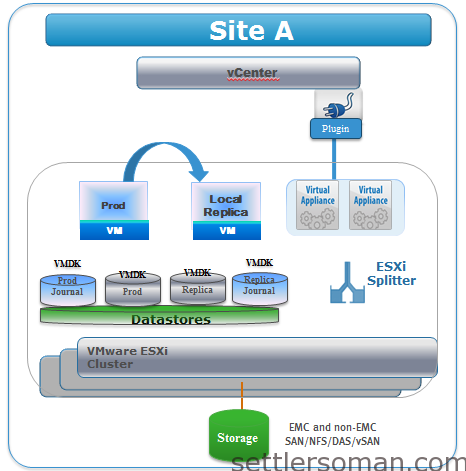
RP4VM has three basic components:
The RecoverPoint virtual appliance (vRPA) - delivered in OVA format and manages all aspects of data replication. vRPA can be grouped as cluster (2-8 vRPAs). There are one or two clusters in a RecoverPoint for VMs system; one cluster is used for local replication and two are used for remote replication.
The RecoverPoint Splitter is proprietary software installed on every ESXi server in an ESXi cluster involved in RecoverPoint replication or running virtual RPAs. The RecoverPoint for VMs splitter splits every write to the VMDK and sends it first to the vRPA.
RecoverPoint for VMs Plugin for vSphere Web Client enables the management of RecoverPoint from vSphere UI and supported on 5.1 and 5.5 vSphere.
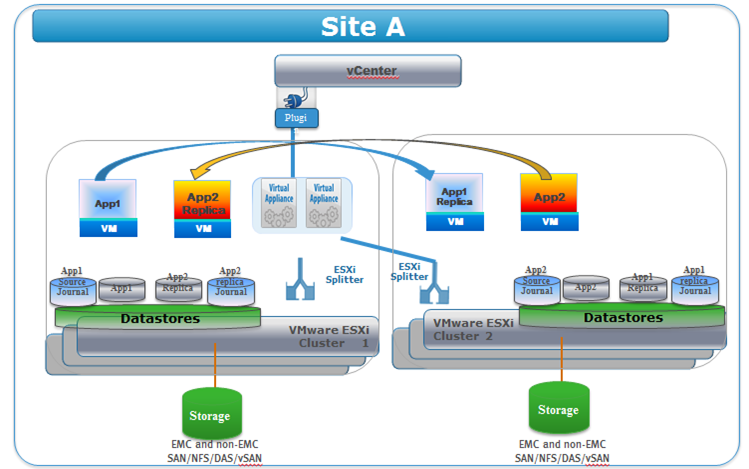
There are available three types of copies:
- Production copy consists of all of the virtual machines with their application data that are the source for replication.
- Local copy is a copy of production virtual machines with their application data that is accessible on the vRPA cluster running production. The local copy is used for continuous data protection, such as recovering from logical errors and data corruption.
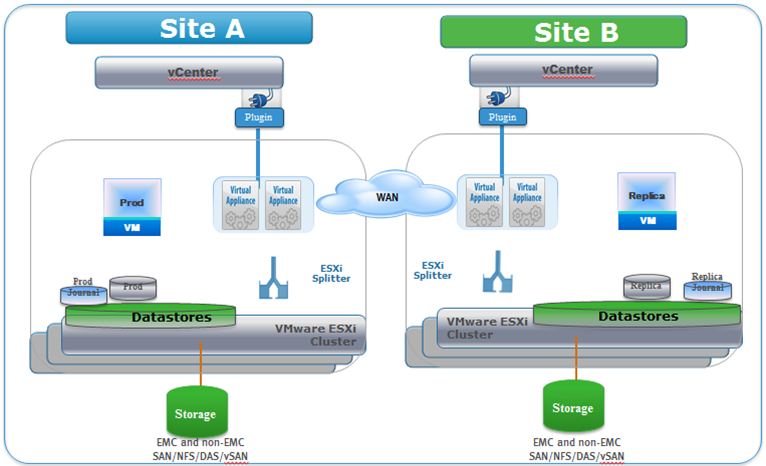
- Remote copy is a copy of production virtual machines with their application data that is accessible on a remote vRPA cluster. ( Remote denotes clusters that are connected only by WAN.) The remote copy is used for disaster recovery.
There are available three ways of protection:
Note: To find out how to deploy RecoverPoint please follow my another article How to deploy RecoverPoint for Virtual Machines 4.2?
EMC release the next version of EMC RevoverPoint for Virtual Machines (RP4VM) - version 4.3.