I was going to write this post a long time ago and I postponed it many times. Today during a configuration of VMware VMs backup by NetBackup for my customer, again I have met a situation where ESXi hosts were added using IP address. In this post let's discuss pros and cons of this design considerations.
ESXi hosts can be added to vCenter inventory (datacenter/cluster) using IP address or hostname/FQDN. So when and why ESXi hosts could be added using IP address? I was thinking about it and one idea came to my mind: no DNS server available 🙂 But is this really the problem? No, because it is possible to use /etc/hosts (vCenter Appliance) or hosts file (Windows) to map FQDN of ESXi to IP address. What does happen when you use IP address? Generally, you could be lucky and nothing happens 🙂 However, I have faced few times a problem with backup of VMware VMs when you need to use a different VMkernel. For example, you have two VMkernels: the first one used just for management, the second one used for storage and backup traffic. Generally, a backup application talks with vCenter as follow (backup over LAN):
- Hello vCenter, I would like to backup a VM1. Where is it located?
- vCenter sends back: hello backup application. I have done a snapshot and the VM1 is located on ESXi-06 or 192.168.0.55 (depends on how ESXi is added to vCenter).
- The backup application talks directly with ESXi now: Hello ESXi-06, I would like to copy a snapshot of VM1 🙂
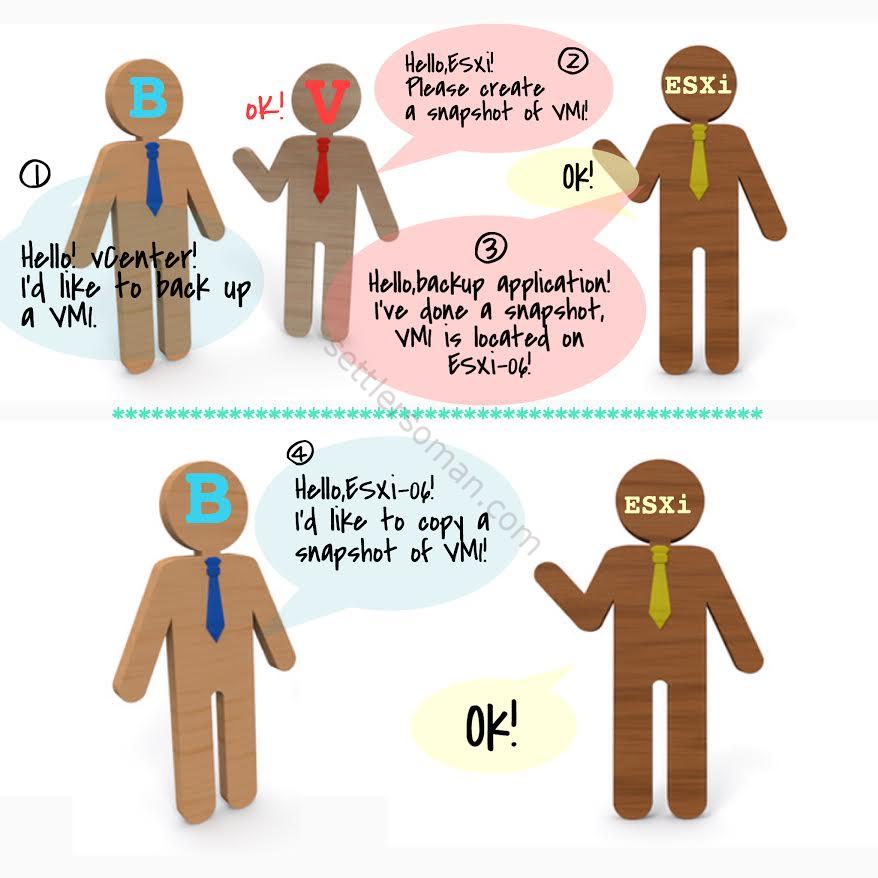
Backup stages.
As you can see above, if you use IP address of ESXi to add to vCenter, you can not change how the backup traffic is sent (which VMkernel is used) between ESXi and backup application. If you use a name (FQDN), you can always overwrite a name locally on the backup server (edit hosts file or /etc/hosts) and force backup application to talk with ESXi using another VMkernel. I described this in a post about VADP VMkernel design.
So to sum up - ESXi FQDN hostname:
Pros:
- easy to manage because it is easier to remember a name than IP address.
- many additional applications check FQDN resolve.
- useful to use a different VMkernel interface for backup traffic.
Cons:
- DNS Server required or manual edit of the hosts file
ESXi IP address:
Pros:
- easy configuration, just add to vCenter 😉
- no DNS Server required or edit of the hosts file
Cons:
- not possible to specify another VMkernel interface for backup traffic
- changing of ESXi IP address requires modification in vCenter (remove and add ESXi host from/to the vCenter)
Please remember, if you use IP address to join ESXi host to the vCenter, you can just disconnect the ESXi hosts from the vCenter. Then remove it and add again by using FQDN. This procedure should not require any VMs to be shut down or rebooted 🙂