As a settler in the SDDC world 🙂 I can't miss a key product in the software
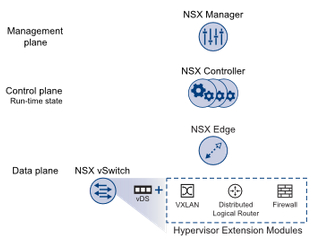
- Data Plane
- Control Plane
- Management Plane
Above components are the most important. There is also one more component - Consumption Plane = e.g. integration with vRealize Automation, vCloud Director.
NSX Management Plane
The NSX management plane is based on the NSX Manager. This is a virtual appliance (deployed as a standard OVF template on an ESXi host - recommended using the Management Cluster) pointed to vCenter (1:1 relationship. If you have a cross-vCenter NSX environment that I described some days ago, there is also one-to-one relationship). NSX Manager is responsible for controlling and managing the whole virtual network by:
- centralizing network management,
- providing REST APis for creating, configuring and monitoring NSX components such as logical switches or edge services gateways.
NSX Control Plane
The NSX control plane is based on NSX Controller cluster. NSX Controller is also a virtual appliance (must be deployed in a three-node cluster for high availability and scale) that is responsible for managing the distributed switching and routing modules in ESXi hosts. The controller does not have any dataplane traffic passing through it.
The NSX controller is the central control point for all logical switches within a network and maintains information of all virtual machines, hosts, logical switches, and VXLANs.
NSX Data Plane
The NSX data plane is: NSX vSwitch = vSphere Distribued Switch (VDS) + kernel modules (such as VXLAN, Distributed Logical Router or Firewall). 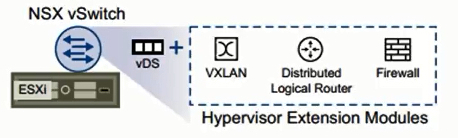 NSX vSwitch provides access-level switching in ESXi host. The logical router provides L2 bridging from the logical networking space (VXLAN) to the physical network (VLAN). The NSX Edge gateway connects isolated, stub networks to shared (uplink) networks by providing common gateway services such as dynamic routing, perimeter firewall, DHCP, VPN, NAT, and Load Balancing.
NSX vSwitch provides access-level switching in ESXi host. The logical router provides L2 bridging from the logical networking space (VXLAN) to the physical network (VLAN). The NSX Edge gateway connects isolated, stub networks to shared (uplink) networks by providing common gateway services such as dynamic routing, perimeter firewall, DHCP, VPN, NAT, and Load Balancing.
NSX Services
There are NSX services as follows:
- Logical Switches - a distributed switches that can span vSphere clusters. Each mapped to a unique VXLAN and also can be extended to a physical device using an L2 bridge.
- Logical Routers
- Logical Firewall - a hypervisor kernel-embedded firewall.
- Logical VPNs
- Logical Load Balancer
- Service Composer - grouping and mapping services to applications
- NSX Extensibility - integration with 3rd-party solutions.
I will write a dedicated post about above services. Please stay tuned! 🙂
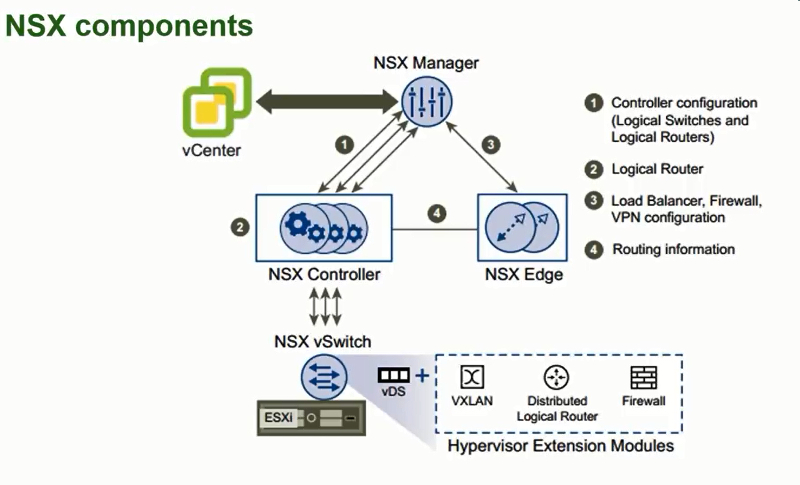
NSX components interaction
To sum up, the following figure presents interaction between NSX components:
For more information, please follow VMware NSX official documentation.